COMPARISONS MODEL PROJECT
NUHA MIAN


| STRUCTURE | FUNCTION |
|---|---|
| CELL MEMBRANE | The cell membrane is a thin fluid made up of phospholipid bilayers that surrounds the cells. It is used to separate the inside of cells from the outside (mainly separates cytoplasm from the outside). It is located around the cytoplasm. |
| CENTRIOLES | the Centrioles are a small set of tube-like organelles that play a part in cell division to help animals reproduce. |
| CYTOPLASM | The cytoplasm is a Jelly-like substance that keeps the parts of the cell together as a way of protecting them. |
| Endoplasmic reticulum | The Endoplasmic reticulum is a connection of tubes that make and transport proteins and fats to the cell. |
| Golgi apparatus | the golgi apparatus Stores and processes proteins and lipid molecules to transport to the other parts of the cell. |
| lysosomes | lysosomes are organelles made up of digestive enzymes that break down dying or extra unneeded cells when they are damaged. |
| Mitochondrion | the mitochondrion is an organelle that creates energy to power the cell. |
| Nuclear membrane | the nuclear membrane Separates chromosomes from the rest of the cell around the nucleus and allows acids and proteins to pass through between the nucleus and cytoplasm. |
| nucleolus | the Nucleolus is the part of the cell where ribosomes are created. |
| nucleus | the nucleus is the area where genetic information is stored and includes ‘Instructions’ / genetic code on how the cell should function. |
| ribosomes | ribosomes are organelles that create new proteins based on the instructions from the nucleus. |
| vacuole | the vacuole Stores nutrients for the cell and filters out harmful substances / waste from entering the cell. |
| vesicles | vesicles are Small structures that transport ribosomes proteins and other nutrients cells need to the golgi apparatus. the vesicles are also the area where ribosomes are created in the nucleus. |
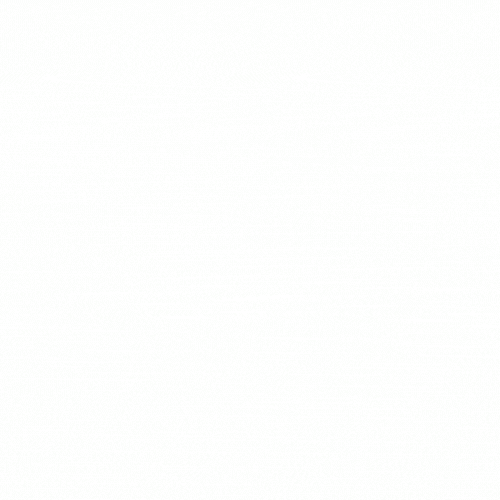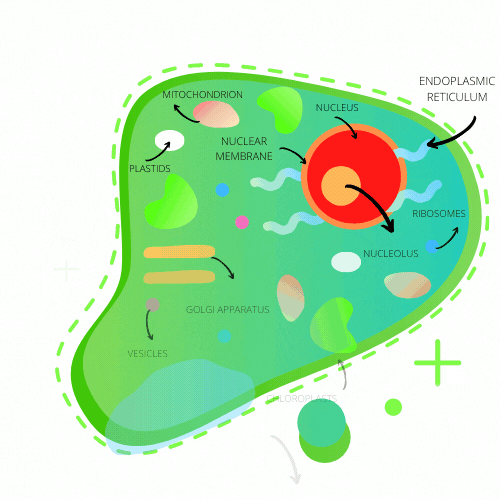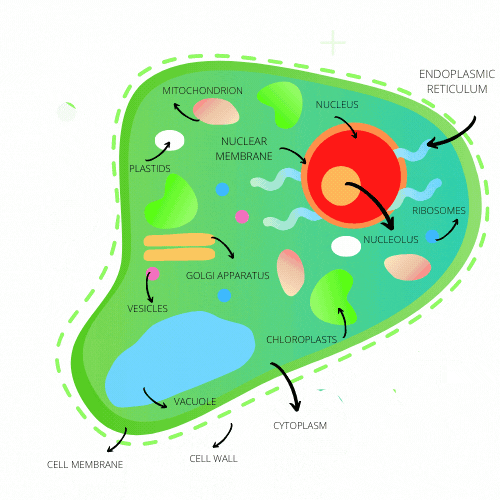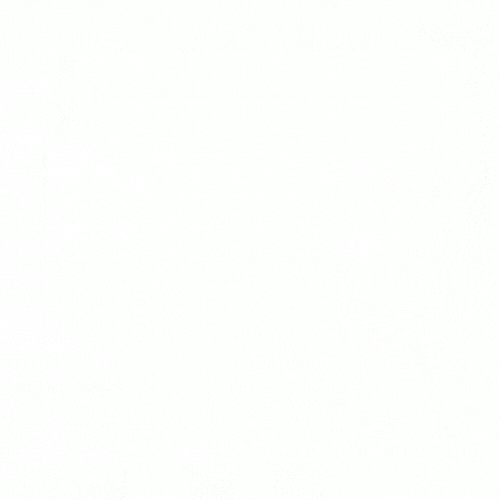

| STRUCTURE | FUNCTION |
|---|---|
| CELL MEMBRANE | The cell membrane is a thin fluid made up of phospholipid bilayers that surrounds the cells. It is used to separate the inside of cells from the outside (mainly separates cytoplasm from the outside). It is located BETWEEN THE CYTOPLASM AND CELL WALL. |
| Cell wall | THE CELL WALL IS A Strong layer made up of fibers that protects the cell AND helps IT hold ITS shape WHILE filterING through toxic molecules. |
| Chloroplast | THE CHLOROPLAST IS THE organelle responsible for converting energy to nutrients (photosynthesis) FOR THE PLANT CELL. |
| CYTOPLASM | The cytoplasm is a Jelly-like substance that keeps the parts of the cell together as a way of protecting tHEM AS WELL AS GIVING THE CELL ITS SHAPE. |
| Endoplasmic reticulum | The Endoplasmic reticulum is a connection of tubes that make and transport proteins and fats to the cell. |
| Golgi apparatus | the golgi apparatus Stores and processes proteins and lipid molecules to transport to the other parts of the cell. |
| Mitochondrion | the mitochondrion is an organelle that creates energy to power the cell. |
| Nuclear membrane | the nuclear membrane Separates chromosomes from the rest of the cell around the nucleus and allows acids and proteins to pass through between the nucleus and cytoplasm. |
| nucleolus | the Nucleolus is the part of the cell where ribosomes are created. |
| nucleus | the nucleus is the area where genetic information is stored and includes ‘Instructions’ / genetic code on how the cell should function. |
| ribosomes | ribosomes are organelles that create new proteins based on the instructions from the nucleus. |
| vacuole | the vacuole Stores nutrients for the cell and filters out harmful substances / waste from entering the cell while helping the plant keep its shape. |
| vesicles | vesicles are Small structures that transport ribosomes proteins and other nutrients cells need to the golgi apparatus. the vesicles are also the area where ribosomes are created in the nucleus. |
| plastids | the plastid is an organelle that stores and creates nutrients for the plants as well as holding pigments that are used for photosynthesis. |

similarities
cell membrane
centrioles
cytoplasm
endoplasmic reticulum
golgi apparatus
mitochondrion
nuclear membrane
nucleolus
nucleus
ribosomes
vacuole
vesicles
DIFFERENCES
plant cells:
cell wall
chloroplast
plastids
animal cells:
lysosomes
Works Cited
Kiddle. "Centriole." Kiddle Encyclopedia, 15 Jan. 2020, kids.kiddle.co/Centriole.
---. "Nucleolus." Kiddle Encyclopedia, 23 Dec. 2020, kids.kiddle.co/Nucleolus.
---. "Vacuole." Kiddle Encyclopedia, 4 June. 2020,
kids.kiddle.co/Vacuole.
Kiddle Encyclopaedia. "Cell Membrane Facts." Kiddle, 23 Dec. 2020, kids.kiddle.co/Cellmembrane.
National Human Genome Research Institute. "Golgi Body." Genome GOV, www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/golgi-body#:~:text=A%20Golgi%20body%2C%20also%20known,a%20series%20of%20stacked%20membranes.
---. "Mitochondrion." Genome GOV, www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Mitochondria#:~:text=Mitochondria%20are%20membrane%2Dbound%20cell,called%20adenosine%20triphosphate%20(ATP).
---. "Nuclear Membrane." Genome GOV, www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Nuclear-Membrane#:~:text=A%20nuclear%20membrane%20is%20a,between%20the%20nucleus%20and%20cytoplasm.
Softschools. "Function of Cytoplasm." SoftSchools.com, www.softschools.com/science/biology/functionof_cytoplasm/.
"Endoplasmic Reticulum Lesson for Kids: Definition & Function." Study.com, 23 October 2017, study.com/academy/lesson/endoplasmic-reticulum-lesson-for-kids-definition-function.html